Multi-phase PMSM Model#
Important:
The multi-phase PMSM IP-cores are based on the three-phase PMSM Model IP-core, where the basics (e.g. working principle of the integrations is explained)
There are two mulit-phase IP-cores, a six-phase and a nine-phase one
Differences to the three-phase PMSM model IP-core:
IP-Cores model a six-phase and nine-phase PMSM
Sample frequency of the integrator is \(T_s=\frac{1}{1\,MHz}\)
IP-Core clock frequency must be \(f_{clk}=100\,MHz\)!
All calculations in the IP-Core are done in double precision
Interfaces to PL are realized in fixedpoint, while interfaces to the PS use single precision float values
System description#
The modelling of the multi-phase machine is based on [[1]]. The general idea in this work and also the common approach to model multi-phase machines is, to transform the phase variables with the VSD and Park transformations, as shown and done in Multi-phase VSD and Park transformation IP-Core and Coordinate Transformation. Transformed voltages are used as input for this IP-core and the outputs will also be in the rotary or stationary reference frame ant not phase variables. This IP-core contains the electric differential equations and the mechanical part, where the torque is calculated. Additionally, either a torque load or a fixed speed can be set to test the machine model. While the equations are mostly similar to the ones of the three-phase PMSM Model, they will be shown here again for the sake of completeness. To obtain more details about the equations and integrators, reading PMSM Model is advised.
dq equations#
Mechanical equations#
Note that the integrator for \(\theta_{el}\) is limited to \(\pm \pi\) to avoid overflow (wrapping integrator).
Additional system equations#
Six-phase model#
Nine-phase model#
IP-core interfaces#
Port Name |
Port Type |
Data Type |
Interface |
Range |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
reset_integrators |
Input |
boolean |
AXI 0x100 |
resets all integrators |
|
use_axi_input |
Input |
boolean |
AXI 0x104 |
true: use AXI voltage values as input; false: use PL voltage values as input |
|
simulate_mechanical |
Input |
boolean |
AXI 0x108 |
true: load simulation; false: fix PMSM speed |
|
load_torque |
Input |
single |
AXI 0x10C |
load torque if simulate_mechanical is true |
|
omega_mech |
Input |
single |
AXI 0x110 |
fixed speed if simulate_mechanical is false |
|
physical_parameters |
Input |
single bus (12/15) |
AXI 0x114-0x170 |
set machine parameters; description see “uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_config_t”/ “uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_config_t” struct |
|
voltage_input_dq_axi |
Input |
single vector (6/9) |
AXI 0x180-0x1A0 |
input voltages as transformed values in the form of “uz_6ph_dq_t”/ “uz_9ph_dq_t” from AXI |
|
voltage_input_dq |
Input |
sfix27_En16 vector (6/9) |
External Signal |
-1024 to 1023 |
input voltages as transformed values in the form of “uz_6ph_dq_t”/ “uz_9ph_dq_t” from PL |
theta_el_out_axi |
Output |
single |
AXI 0x14C |
\(\pm \pi\) |
actual electric rotor angle |
theta_el_out |
Output |
sfix18_En14 |
External Signal |
\(\pm \pi\) |
actual electric rotor angle |
M_Mi_out_axi |
Output |
single |
AXI 0x174 |
actual machine torque |
|
omega_mech_out_axi |
Output |
single |
AXI 0x178 |
actual machine speed |
|
omega_mech_out |
Output |
sfix24_En11 |
External Signal |
-4096 to 4095 |
actual machine speed |
currents_dq_out_axi |
Output |
single vector (6/9) |
AXI 0x200-0x220 |
actual currents in the rotary or stationary reference frame to AXI in the form of “uz_6ph_dq_t”/ “uz_9ph_dq_t” |
|
currents_dq_out |
Output |
sfix27_En18 vector (6/9) |
External Signal |
-256 to +255 |
actual currents in the rotary or stationary reference frame to PL in the form of “uz_6ph_dq_t”/ “uz_9ph_dq_t” |
voltage_input_dq_out_axi_fb |
Output |
single vector (6/9) |
AXI 0x280-2A0 |
feedback actual input voltages to AXI (available for use_axi_input true and false) |
Driver reference#
The set and get functions for voltage and currents are implemented as normal and unsafe version.
In addition to the regular functions, unsafe versions of the driver exist (_unsafe).
These functions are considerably faster than their safe counterparts but violate the software rules outlined in Software Development Guidelines.
It is strongly advised to manually test by comparing the safe and unsafe versions before using _unsafe!””
Six-phase model#
-
typedef struct uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t#
Object data type definition of the PMSM model IP-Core driver.
-
struct uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_config_t#
Configuration struct for the PMSM model IP-Core driver.
Public Members
-
uint32_t base_address#
Base address of the IP-Core instance to which the driver is coupled
-
uint32_t ip_core_frequency_Hz#
Clock frequency of IP-Core
-
float polepairs#
Polepairs of the PMSM
-
float r_1#
Stator resistance in ohm
-
uz_6ph_dq_t inductance#
Subsystem inductances
-
float psi_pm#
PM flux linkage
-
float friction_coefficient#
Linear coefficient of friction
-
float coulomb_friction_constant#
Static friction constant
-
float inertia#
Inertia of the PMSM
-
bool simulate_mechanical_system#
Determine if mechanical system is simulated or speed is an input
-
bool switch_pspl#
true: inputs from PS, false: inputs from PL
-
uint32_t base_address#
-
struct uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_outputs_general_t#
Struct to return and read the general outputs of the PMSM Model.
-
uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_init(struct uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_config_t config)#
Initialize an instance of the driver.
- Parameters:
config – Config struct
- Returns:
uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t* Pointer to an initialized instance of the driver
-
void uz_pmsm_model6ph_trigger_voltage_input_strobe(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self)#
Takes the values of the AXI shadow register and pass them to the actual input.
- Parameters:
self –
-
void uz_pmsm_model6ph_trigger_voltage_output_strobe(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self)#
Takes the values of the shadow register and pass them to the actual AXI register.
- Parameters:
self –
-
void uz_pmsm_model6ph_trigger_current_output_strobe(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self)#
Takes the values of the shadow register and pass them to the actual AXI register.
- Parameters:
self –
-
void uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_set_inputs_general(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self, float omega_mech, float load_torque)#
Set general inputs of the model and write them to the PMSM model.
- Parameters:
self – Pointer to driver instance
omega_mech – value for fixed omega if uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_config_t.simulate_mechanical_system is false
load_torque – value for load torque if uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_config_t.simulate_mechanical_system is true
-
struct uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_outputs_general_t uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_get_outputs_general(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self)#
Returns general outputs of PMSM model.
- Parameters:
self – Pointer to driver instance
- Returns:
struct uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_outputs_general_t output values
-
void uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_set_voltage(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self, uz_6ph_dq_t voltages)#
Safe function to set the input voltages of PMSM if PS is selected as source for voltages.
- Parameters:
self –
voltages – struct of type uz_6ph_dq_t containing the voltages to set
-
void uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_set_voltage_unsafe(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self, uz_6ph_dq_t voltages)#
Unsafe function to set the input voltages of PMSM if PS is selected as source for voltages.
- Parameters:
self –
voltages – struct of type uz_6ph_dq_t containing the voltages to set
-
uz_6ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_get_input_voltages(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self)#
Safe function to read out the set input voltages of PMSM. Works for voltages coming from PS and PL.
- Parameters:
self –
- Returns:
struct of type uz_6ph_dq_t containing the set voltages
-
uz_6ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_get_input_voltages_unsafe(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self)#
Unsafe function to read out the set input voltages of PMSM. Works for voltages coming from PS and PL.
- Parameters:
self –
- Returns:
struct of type uz_6ph_dq_t containing the set voltages
-
uz_6ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_get_output_currents(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self)#
Safe function to read out the actual currents of PMSM.
- Parameters:
self –
- Returns:
struct of type uz_6ph_dq_t containing the actual currents
-
uz_6ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_get_output_currents_unsafe(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self)#
Unsafe function to read out the actual currents of PMSM.
- Parameters:
self –
- Returns:
struct of type uz_6ph_dq_t containing the actual currents
-
void uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_reset(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self)#
Resets the PMSM model by writing zero to all PS inputs and sets integrators to zero.
- Parameters:
self – Pointer to driver instance
-
void uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_set_use_axi_input(uz_pmsm_model6ph_dq_t *self, bool use_axi)#
Change input source for voltages (PL or PS) during runtime.
- Parameters:
self – Pointer to driver instance
use_axi – true: voltages from PS, false: voltages from PL
Nine-phase model#
-
typedef struct uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t#
Object data type definition of the PMSM model IP-Core driver.
-
struct uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_config_t#
Configuration struct for the PMSM model IP-Core driver.
Public Members
-
uint32_t base_address#
Base address of the IP-Core instance to which the driver is coupled
-
uint32_t ip_core_frequency_Hz#
Clock frequency of IP-Core
-
float polepairs#
Polepairs of the PMSM
-
float r_1#
Stator resistance in ohm
-
uz_9ph_dq_t inductance#
Subsystem inductances
-
float psi_pm#
PM flux linkage
-
float friction_coefficient#
Linear coefficient of friction
-
float coulomb_friction_constant#
Static friction constant
-
float inertia#
Inertia of the PMSM
-
bool simulate_mechanical_system#
Determine if mechanical system is simulated or speed is an input
-
bool switch_pspl#
true: inputs from PS, false: inputs from PL
-
uint32_t base_address#
-
struct uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_outputs_general_t#
Struct to return and read the general outputs of the PMSM Model.
-
uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_init(struct uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_config_t config)#
Initialize an instance of the driver.
- Parameters:
config – Config struct
- Returns:
uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t* Pointer to an initialized instance of the driver
-
void uz_pmsm_model9ph_trigger_voltage_input_strobe(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self)#
Takes the values of the AXI shadow register and pass them to the actual input.
- Parameters:
self –
-
void uz_pmsm_model9ph_trigger_voltage_output_strobe(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self)#
Takes the values of the shadow register and pass them to the actual AXI register.
- Parameters:
self –
-
void uz_pmsm_model9ph_trigger_current_output_strobe(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self)#
Takes the values of the shadow register and pass them to the actual AXI register.
- Parameters:
self –
-
void uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_set_inputs_general(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self, float omega_mech, float load_torque)#
Set general inputs of the model and write them to the PMSM model.
- Parameters:
self – Pointer to driver instance
omega_mech – value for fixed omega if uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_config_t.simulate_mechanical_system is false
load_torque – value for load torque if uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_config_t.simulate_mechanical_system is true
-
struct uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_outputs_general_t uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_get_outputs_general(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self)#
Returns general outputs of PMSM model.
- Parameters:
self – Pointer to driver instance
- Returns:
struct uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_outputs_general_t output values
-
void uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_set_voltage(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self, uz_9ph_dq_t voltages)#
Safe function to set the input voltages of PMSM if PS is selected as source for voltages.
- Parameters:
self –
voltages – struct of type uz_9ph_dq_t containing the voltages to set
-
void uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_set_voltage_unsafe(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self, uz_9ph_dq_t voltages)#
Unsafe function to set the input voltages of PMSM if PS is selected as source for voltages.
- Parameters:
self –
voltages – struct of type uz_9ph_dq_t containing the voltages to set
-
uz_9ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_get_input_voltages(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self)#
Safe function to read out the set input voltages of PMSM. Works for voltages coming from PS and PL.
- Parameters:
self –
- Returns:
struct of type uz_9ph_dq_t containing the set voltages
-
uz_9ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_get_input_voltages_unsafe(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self)#
Unsafe function to read out the set input voltages of PMSM. Works for voltages coming from PS and PL.
- Parameters:
self –
- Returns:
struct of type uz_9ph_dq_t containing the set voltages
-
uz_9ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_get_output_currents(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self)#
Safe function to read out the actual currents of PMSM.
- Parameters:
self –
- Returns:
struct of type uz_9ph_dq_t containing the actual currents
-
uz_9ph_dq_t uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_get_output_currents_unsafe(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self)#
Unsafe function to read out the actual currents of PMSM.
- Parameters:
self –
- Returns:
struct of type uz_9ph_dq_t containing the actual currents
-
void uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_reset(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self)#
Resets the PMSM model by writing zero to all PS inputs and sets integrators to zero.
- Parameters:
self – Pointer to driver instance
-
void uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_set_use_axi_input(uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *self, bool use_axi)#
Change input source for voltages (PL or PS) during runtime.
- Parameters:
self – Pointer to driver instance
use_axi – true: voltages from PS, false: voltages from PL
Example usage (standalone)#
The IP-core has two intended use cases:
Using the model in the dq domain only with inputs coming from the PS
Simulating a complete multi-phase drive system including the Inverter Model, Multi-phase VSD and Park transformation IP-Core (see the CIL examples in CIL PMSM)
Using the IP-core in PS only is similar to the use cases shown in PMSM Model open loop example which is recreated here. The placement of the IP-core for the use from PS only is straight forward as only the default PL interfaces have to be connected. For the example the nine-phase model is used, but the same can also be applied for the six-phase model.
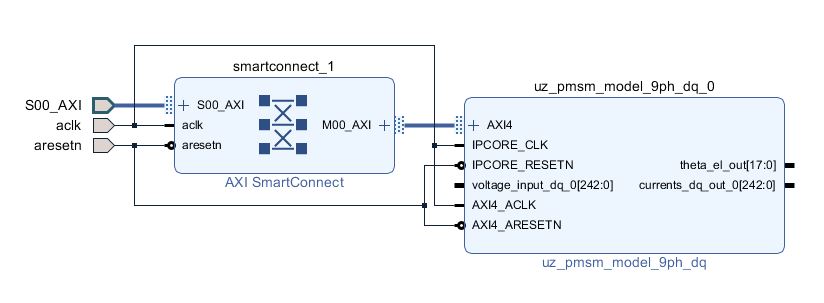
Fig. 363 Test setup for IP-core PS test in Vivado#
The following code is used in main.c (initialization) and isr.c (application):
#include "IP_Cores/uz_pmsm_model_9ph_dq/uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq.h"
uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *pmsm=NULL;
struct uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_config_t pmsm_config = { // example config values
.base_address=XPAR_UZ_PMSM_MODEL_0_BASEADDR,
.ip_core_frequency_Hz = 100000000U,
.polepairs = 3.0f,
.r_1 = 31.3f,
.inductance.d = 0.46f,
.inductance.q = 0.46f,
.inductance.x1 = 0.08f,
.inductance.y1 = 0.08f,
.inductance.x2 = 0.08f,
.inductance.y2 = 0.08f,
.inductance.x3 = 0.08f,
.inductance.y3 = 0.08f,
.inductance.zero = 0.08f,
.psi_pm = 0.072f,
.friction_coefficient = 0.001f,
.coulomb_friction_constant = 0.001f,
.inertia = 0.001f,
.simulate_mechanical_system = false,
.switch_pspl = true};
// .. rest of the code in main.c before loop
int main(void)
// ..
case init_ip_cores: // default line from main.c
pmsm = uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_init(pmsm_config);
#include "../IP_Cores/uz_pmsm_model_9ph_dq/uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq.h"
extern uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_t *pmsm; // pointer to PMSM object
struct uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_outputs_general_t out_general = {0}; // stores general outputs
uz_9ph_dq_t in_voltages = { // stores input voltages (set random voltages for testing)
.d = 1.0f,
.q = 2.0f,
.x1 = 3.0f,
.y1 = 4.0f,
.x2 = 5.0f,
.y2 = 6.0f,
.x3 = 7.0f,
.y3 = 8.0f,
.zero = 9.0f};
uz_9ph_dq_t out_currents = {0}; // stores output currents
float omega_mech = 10.0f; // fixed speed can be set from Expressions with this variable
int reset = 0; // use reset variable to reset integrators from Expressions
// .. rest of the code in isr.c before loop
void ISR_Control(void *data)
// ..
update_speed_and_position_of_encoder_on_D5(&Global_Data); // default line from isr.c
if(reset)
uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_reset(pmsm); // use reset variable to reset integrators from Expressions
uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_set_inputs_general(pmsm,omega_mech,0.0f); // set fixed speed, because load simulation is disabled by pmsm_config.simulate_mechanical_system
uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_set_voltage(pmsm,in_voltages); // set input voltage
out_general = uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_get_outputs_general(pmsm); // read out resulting general outputs
out_currents = uz_pmsm_model9ph_dq_get_output_currents(pmsm); // read out actual currents
To prove functionality, the output currents of the shown example are evaluated. The resulting machine torque is \(-0.01562337\,Nm\) an the resulting currents are shown in the following equation. The results were recreated with the Simulink model.