How to docs#
The documentation for the UltraZohm uses https://www.sphinx-doc.org. Sphinx creates the documentation pages in html based on text files. These text files use reStructuredText (RST) as a markup language. Sphinx takes the different RST files and builds them to the docs page. The documentation is hosted on a web server, the build and deployment is handled by the build pipeline.
Note
The online version on docs.ultrazohm.com is always the documentation of the main branch. If you build the documentation locally, you build the documentation of the specific branch that you have checked out! Building the documentation locally is useful for writing the documentation and getting a preview of the changes.
Installation#
Tip
Use the VS Code Remote Container to handle all installations for you instead of installing all dependencies on your machine and keeping them up to date! Using the VS Code Remote Container is strongly recommended!
To build and edit the documentation on your native system, you need to:
Install Python
Install pip (included in current python versions)
Install everything in the
requirements.txtin/docsby invokingpip install -r requirements.txtin a command shell inside/docsInstall everything required for the extension
sphinxcontrib.tikz. Follow their install guide!As image processing
suiteyou have to install GhostscriptAssuming standard installation path the include path for Ghostscript is:
C:\Program Files\gs\gs9.54.0\bin(Windows)
Install everything required for the extension
Breathe(connects Doxygen to sphinx. Install guide!Build Doxygen by invoking
make doxygenin a shell inside/docsBuild the documentation by invoking
make htmlYou can open the docs in
/docs/build/html/index.htmlYou can edit the documentation by using a text editor of your choice
Tip
Sometimes you might need to clean the output with make clean or generate clean build with make clean html
Tip
You can use make livehtml instead of make html which opens a new browser that synchronizes live with changes that you make locally (uses sphinx-autobuild).
Tip
Use make docs to build doxygen and the sphinx exactly as it is used in the build pipeline, see Continuous Integration.

Note
If make html or make livehtml do not work due to missing package errors, run pip install -r requirements.txt again. If this does not solve the problem please open an issue.
Makefile reference#
The following commands are available to call with make.
Generating the sphinx documentation requires that Doxygen was already generated.
Command |
Function |
|---|---|
|
deletes sphinx build folder |
|
deletes the Doxygen build folder |
|
builds sphinx documentation |
|
builds Doxygen |
|
builds Doxygen and sphinx |
|
builds sphinx with live preview |
Video#
This video shows how to install python, the requirements, and build the documentation.
Please note that the installation steps for sphinxcontrib.tikz (i.e., Ghostscript and Latex) is not shown in the video since the installation steps depend on your OS.
Please note that the installation steps for breathe (i.e., Doxygen) are not shown in the video since the installation steps depend on your OS.
This video shows how to change something in the documentation, add a new page, commit the changes and create a pull request in Bitbucket.
Write the docs#
See write the docs as a great resource on how to write documentation. A good cheat sheet is located here: * Example usage from Anaconda
Style#
Do:
Keep it simple
Use simple language
Describe the current state
Focus on the interface
Provide examples on how to use the module, software, PCB, …
Provide additional information in a dedicated section
Have a download section with schematics, additional information, …
Use one line per sentence for cleaner git diffs
Don’t:
Write long and complicated sentences
Add unnecessary chatter
Chatter about what might change in the future (exception: roadmap)
Mix interface with rational
Mix implementation details and user interface
Have random download links in text blocks
Have random line breaks in the text
Common functions#
Use the following examples for reference on how to write the docs. Basics:
Structure#
The structure of .rst files is based on indentation with spaces.
These indentations are a vital part of .rst and do not solely exist for visual alignment.
Note
Spaces are recommended for indentation, but tabs may also be used. For tabs, refer to Compatibility issue with Notepad++ and .rst files.
Example
This is a top-level paragraph.
This paragraph belongs to a first-level blockquote. *Indentation is 4 spaces from the previous.*
This paragraph belongs to a second-level blockquote. *Indentation is 4 spaces from the first-level or 8 from the top-level.*
Another top-level paragraph.
This paragraph belongs to a second-level blockquote.
This paragraph belongs to a first-level blockquote. The
second-level blockquote above is inside this first-level
blockquote.
* Level 1
* Level 2
This translates to the following:
This is a top-level paragraph.
This paragraph belongs to a first-level blockquote. Indentation is 4 spaces from the previous.
This paragraph belongs to a second-level blockquote. Indentation is 4 spaces from the first-level, or 8 from the top-level.
Another top-level paragraph.
This paragraph belongs to a second-level blockquote.
This paragraph belongs to a first-level blockquote. The second-level blockquote above is inside this first-level blockquote.
Level 1
Level 2
Code block#
.. code-block:: c
void function(int argv);
void function(int argv);
Figures#
.. _labelName:
.. figure:: figure.svg
Caption.
Refernce:
Reference ::numref:`labelName`.
Math#
Equations can be inline with
:math:`i_1=\sqrt{i_d^2 +i_q^2}`to render \(i_1=\sqrt{i_d^2 +i_q^2}\) using Latex syntaxEquations can also be in a dedicated blocks
.. math::
i_1=\sqrt{i_d^2 +i_q^2}
Numbering and referencing equations using sphinx build in reference system
.. math::
:label: eq_example_number
i_1=\sqrt{i_d^2 +i_q^2}
This text references Eq.1 by using
:eq:`eq_example_number`The build-in sphinx numbering can not label multiple equations, e.g., in align environments
Alternative according to https://www.mail-archive.com/sphinx-users@googlegroups.com/msg04040.html
.. math::
:nowrap:
\begin{align}
i_1 &=\sqrt{i_d^2 +i_q^2} \label{eq_example_1} \\
i_1 &=\sqrt{i_d^2 +i_q^2} \label{eq_example_2}
\end{align}
- :math:`\eqref{eq_example_1}` and :math:`\eqref{eq_example_2}` are the same equations
\(\eqref{eq_example_1}\) and \(\eqref{eq_example_2}\) are the same equations
Links#
`UltraZohm <ultrazohm.com>`_
Mermaid#
You can and should use mermaid to create figures. Mermaid figures are directly inserted into the docs and searchable!
.. mermaid::
graph TD
A[Text]
A --> B[More text]
graph TD
A[Text]
A --> B[More text]
Tables#
For most information, using a .csv table is preferred:
.. csv-table:: table
:file: path_to_table/table.csv
:widths: 50 50 50
:header-rows: 1
Technical details#
The UltraZohm project uses the following extensions to sphinx.
All extensions are listed in ultrazohm_sw/docs/requirements.txt.
- sphinx
Sphinx-doc is the base software to generate the documentation.
- sphinx_rtd_theme
The theme of the documentation
- sphinxcontrib-mermaid
Enables to embed Mermaid graphs.
- sphinxcontrib.yt
Simple embedding of youtube videos.
- six
Provides compatibility between Python 2 and 3, required by some packages.
- sphinx-autobuild
Enable autobuild and reload after changes for local development with
make livehtml- sphinx-issues
Link to issues and pull requests with
:issue:`51`and:pr:`5`, e.g., issue #5`- sphinx-copybutton
Adds a button to the code blocks that copys the content of the block.
- sphinxcontrib-tikz
Adds the possibility to write tikz pictures in the documentation. Example:
.. tikz:: An Example TikZ Directive with Caption
:align: left
\draw[thick,rounded corners=8pt]
(0,0)--(0,2)--(1,3.25)--(2,2)--(2,0)--(0,2)--(2,2)--(0,0)--(2,0);
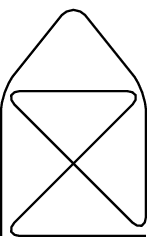
Fig. 28 An Example TikZ Directive with Caption
Alternative to using the Tikz extension for complicated tikz pictures: Create a standalone .tex document with the following boiler plate in an folder called img next the the .rst that includes the picture.
Navigate the the folder of the .tex file using the terminal of the remote container and call pdflatex -shell-escape FILE.tex.
This generates a .svg from the .tex file that can be included as a regular figure.
Add the .tex and the .svg to git since this is currently a manual process.
- breathe
Adds Doxygen documentation to sphinx. See their list of directives. The most common directives are
doxygenfunction,doxygenstruct,doxygentypedef,doxygendefine. See doxygen documentation for how to write Doxygen comments.
Doxygen#
Write Doxygen comments to header files that document the API. Example:
/**
* @brief Converts a signed fixed-point value that is stored as a signed 32-bit integer value to a float.
* This function should only be used directly after reading the int32_t variable from AXI!
*
* @param data Fixed point value stored as a signed 32-bit integer that is read from AXI.
* @param number_of_fractional_bits Number of fractional bits of the data, 31-number_of_fractional_bits is the number of integer bits.
* @return float
*/
static inline float uz_convert_sfixed_to_float(int32_t data, int number_of_fractional_bits) {
uz_assert(number_of_fractional_bits>=0);
return (ldexpf((float) data, -number_of_fractional_bits));
}
Adding the following line to a docs page:
.. doxygenfunction:: uz_convert_sfixed_to_float
Generates the following ouput in the docs:
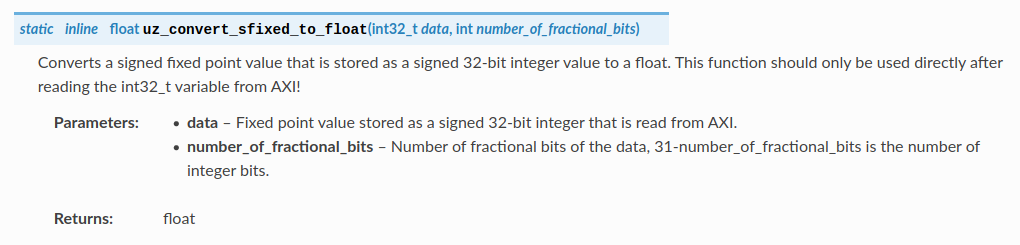
Fig. 29 Example output of Breathe.#
- Examples in docs:
Tip
Note that all types that are used in the function arguments have to be documented, e.g., typedefed variables (see AXI Test IP).
Cards#
Known Issues#
Compatibility issue with Notepad++ and .rst files#
Warning
This is not recommended! Use the VS Code Remote Container instead!
If u edit
.rstfiles in the UltraZohm documentation, an issue whilst using the tabulator key in Notepad++ can occur.If you align the command with the tabulator key in Notepad++, everything looks as its supposed to.
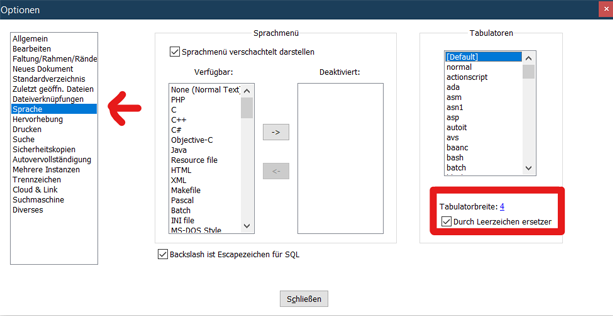
However, if you open the saved file with the tabulator alignment in the normal windows editor, the following is visible.

This wrong alignment via Notepad++ leads to the following error whilst executing make html. You can see the misalignment highlighted in green.
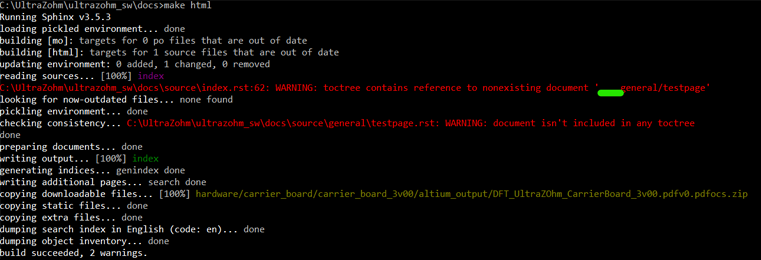
To fix this issue, you can do the following:
In Notepad++ go to Settings → Settings → Language
On the right sight, check the box Replace by space (Durch Leerzeichen ersetzen) and set the Tab size to i.e. 4. 4 spaces is the standard indentation size for different levels.