Software#
Following, the step-by-step setup of the software implementation is shown, to successfully commission the deskbench.
Make sure you complete the whole Getting started section, to guarantee you can flash the UZ and connect to the JavaScope.
Clone the UltraZohm repositories and checkout the feature-branch feature/ZC/Deskbench.
git clone https://bitbucket.org/ultrazohm/ultrazohm_sw.git
git checkout feature/ZC/Deskbench
Open vitis and create the workspace, see Generate the Vitis workspace.
Power up UZ, set the power supply to 48V and a 5A current limit and try to debug the UZ and get a connection to the JavaScope GUI.
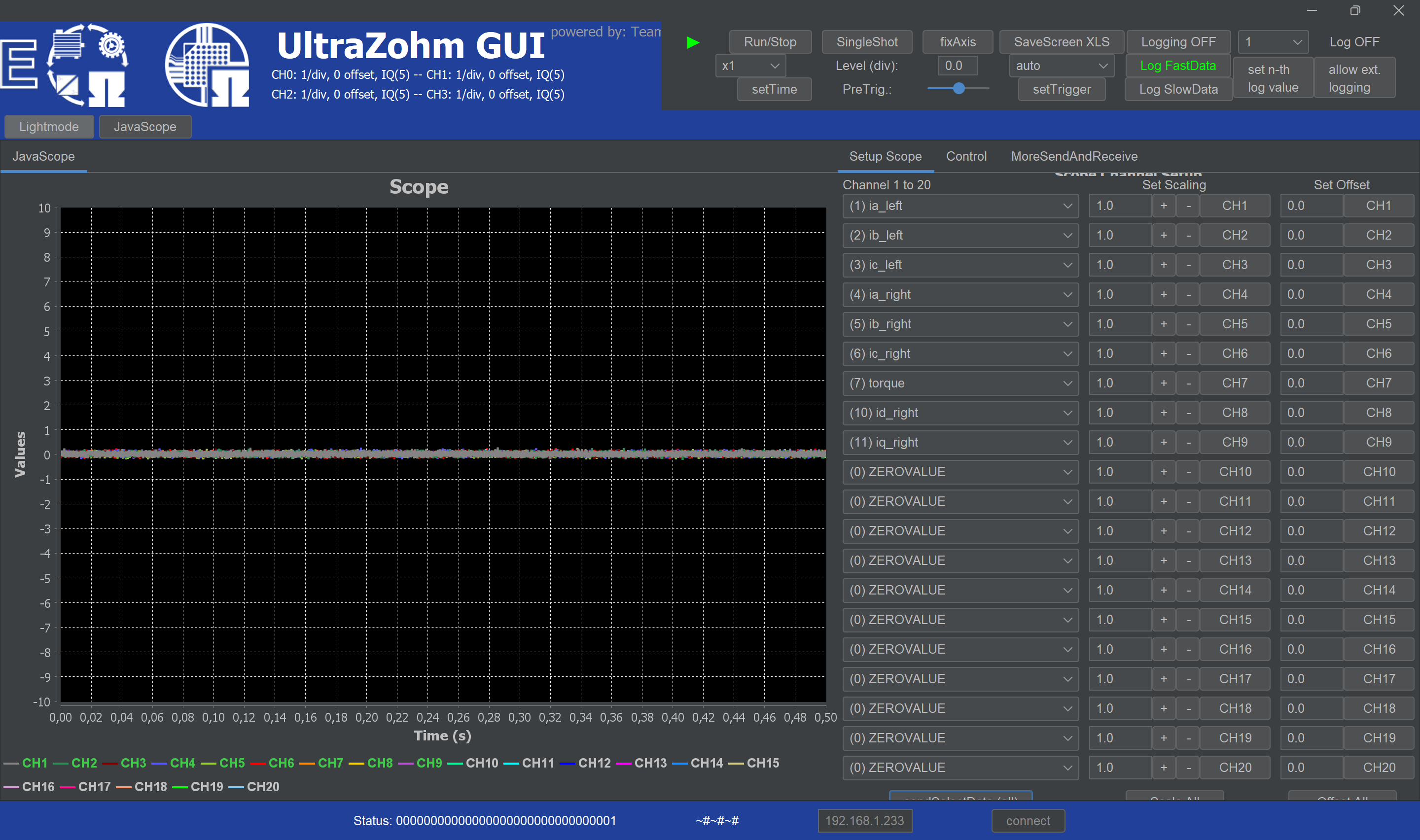
Press
Enable SystemandEnable Control, set a reference speed for the left motor ,e.g. 500 rpm, in the respective input field of the GUI and pressset. Now the load machine should spin at 500 rpm.
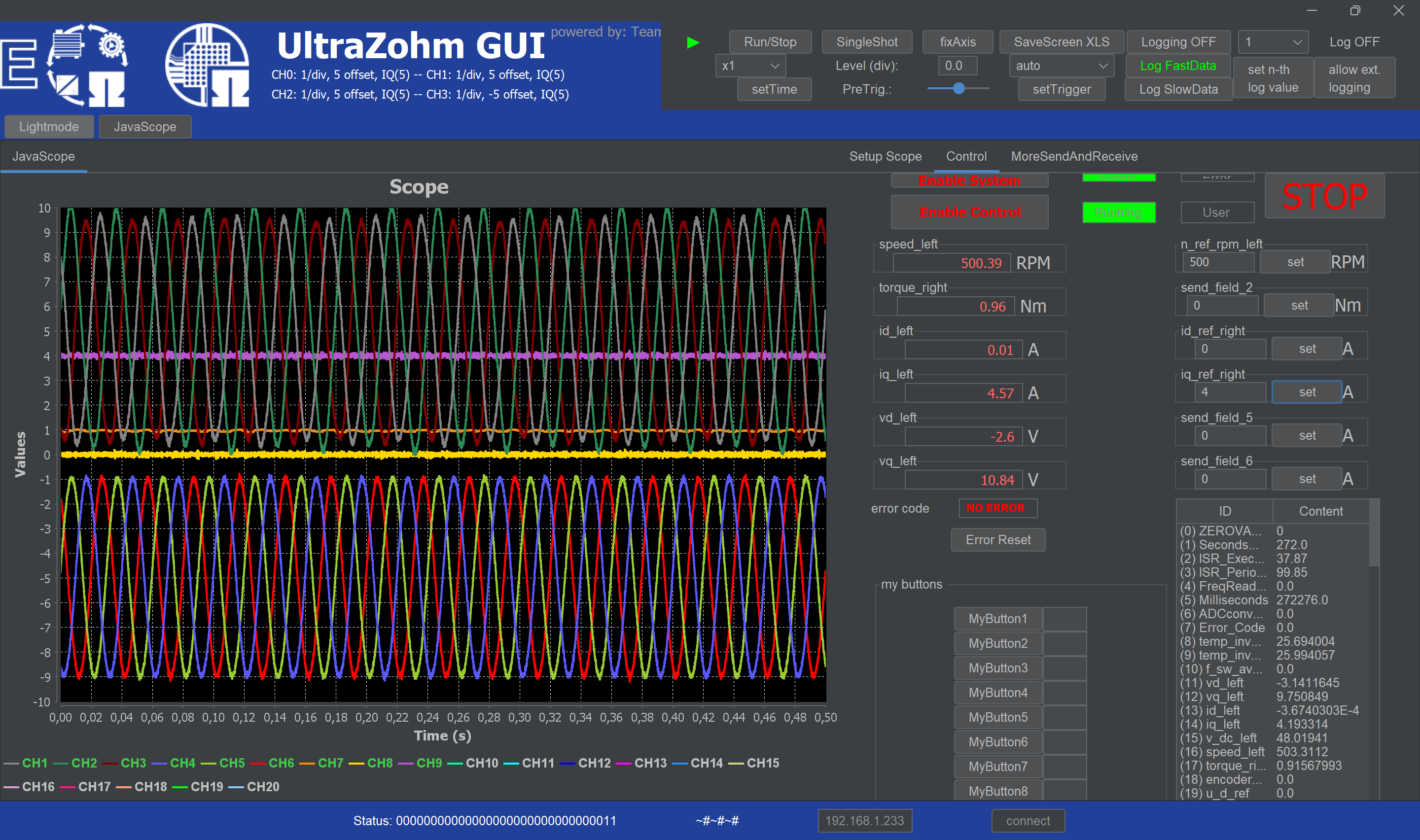
6. Set a q-current reference, e.g. 4A, in the respective input field of the GUI and press set. Now the phase currents, dq-currents and the torque (should be around 1 Nm) are visible in the scope.
For better visibility, the currents have an offset of +-5A.
Now everything is properly setup and the deskbench the user can extend functionality with own algorithms or simply investigate the performance of the implemented control algorithm.
Control structure#
The control structure in software is organized into three components. Two static functions in isr.c handle the control of the left and right motors.
Therefore, the left motor is speed-controlled and serves as the load machine, while the right motor is used for testing algorithms.
The third component is responsible for reading and converting measurement data, such as phase currents.
Several safety features are implemented, such as monitoring current limits and inverter temperatures.
If any of these conditions are met, the UZ transitions into idle_state, resetting all instances and reference values.
Allocation and assigning controller parameters, filters and motor parameter is managed in pi_foc_init.c.
Additionally, controller adjustments can be made in real-time during operation using the Javascope GUI within the MoreSendAndReceive section.